Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
What is the difference between structured and unstructured data?
Structured and unstructured data are two fundamental categories of information that organizations and individuals encounter in the modern data-driven world. Understanding the differences between these types of data is essential, as it affects how data is collected, stored, processed, and analyzed. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the distinctions between structured and unstructured data, their characteristics, significance, and how they are used in various domains.
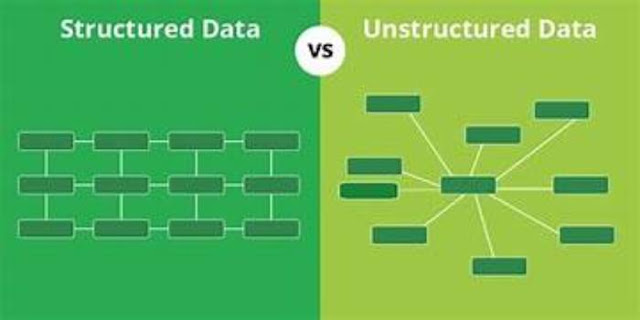
Structured Data:
Structured data refers to information that is organized,
labeled, and stored in a specific format. This format is typically relational
and table-like, making it easy to search, store, and retrieve. Structured data
is highly organized, and its elements are clearly defined, with predefined data
types and relationships. Here are some key characteristics of structured data:
Data Format: Structured data is organized into tables, rows,
and columns, resembling spreadsheets or databases. Each column represents a specific
attribute, and each row contains a unique data entry.
Fixed Schema: It follows a fixed schema or data model, which
means that the data structure is predetermined, and the type of data in each
field is well-defined. This makes it easy to validate and enforce data
integrity.
Relational Databases: Structured data is commonly stored in
relational databases using SQL (Structured Query Language) for querying and
manipulation.
Examples: Examples of structured data include customer
information (name, address, phone number), financial transactions, inventory
lists, and online sales records.
Easy Analysis: Due to its organized nature, structured data
is conducive to quantitative analysis, reporting, and data visualization.
Well-Defined Relationships: Structured data often represents
well-defined relationships between different data elements, which can be
expressed through foreign keys and primary keys in a database.
Structured data plays a crucial role in various industries,
including finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and manufacturing. It is often the
foundation for transactional and operational systems, as well as for business
intelligence and reporting.
Unstructured Data:
Unstructured data, on the other hand, is a form of
information that lacks a predefined structure or schema. It is not easily
organized into tables and does not conform to the conventional row-column
format. Unstructured data is characterized by its complexity, variability, and
abundance. Here are some key characteristics of unstructured data:
No Fixed Format: Unstructured data has no fixed format or
structure, making it more challenging to process and analyze using traditional
database systems.
Diverse Sources: It can originate from diverse sources,
including text, images, audio, video, social media, sensor data, and more.
Varied Content: Unstructured data can contain text, images,
videos, audio recordings, and other multimedia elements. Textual unstructured
data is often the most common and includes documents, emails, social media
posts, and more.
Natural Language: Much unstructured data is in natural
language, which can be highly contextual and nuanced, requiring advanced
language processing techniques for analysis.
No Predefined Schema: Unstructured data lacks a predefined
schema, making it challenging to extract meaning and insights without advanced
data processing methods.
Big Data Challenge: Unstructured data often contributes to
the "big data" challenge, as it is generated and accumulated at a
rapid pace.
Unstructured data poses both opportunities and challenges.
It contains valuable insights, sentiments, and patterns that organizations can
leverage for decision-making, customer analysis, and product development.
However, extracting information from unstructured data often requires
specialized tools and techniques, such as natural language processing (NLP),
computer vision, and machine learning algorithms.
The Significance of Structured and Unstructured Data:
Understanding the significance of structured and
unstructured data is crucial, as it impacts decision-making, technological
choices, and data management strategies.
Decision-Making: Structured data is often used for
day-to-day operational decisions. It provides a clear and well-organized view
of essential business metrics, allowing organizations to make informed choices
based on historical and real-time data. For example, structured data helps
businesses track sales, monitor inventory, and manage financial transactions.
Strategic Insights: Unstructured data is valuable for
gaining strategic insights. It enables organizations to tap into customer
sentiment, market trends, and emerging issues that are not easily discernible
from structured data alone. Social media sentiment analysis and customer
reviews are excellent examples of using unstructured data to understand
customer preferences.
Technological Choices: The nature of the data influences the
technology used for data storage and processing. Structured data is best
managed using traditional relational database systems, while unstructured data
often requires distributed storage and processing solutions like NoSQL
databases and big data platforms.
Data Integration: Many organizations work with a combination
of structured and unstructured data. Integrating these different data types is
essential for a comprehensive view of business operations and customer
interactions.
Compliance and Security: Structured data is generally easier
to manage in terms of compliance and security, as it follows predefined rules
and access controls. Unstructured data, especially sensitive information
contained in documents and emails, requires special attention to maintain data
security and privacy.
Innovation and Competitive Advantage: Leveraging
unstructured data can lead to innovation and competitive advantage.
Organizations that can extract actionable insights from unstructured data have
a better chance of staying ahead in the market.
Use Cases for Structured and Unstructured Data:
Both structured and unstructured data find applications in
various domains and industries. Let's explore some common use cases for each
type of data:
Structured Data Use Cases:
Financial Analysis: Structured data is essential for
financial modeling, risk assessment, and investment analysis.
Inventory Management: Businesses use structured data to
monitor stock levels, track product movement, and optimize supply chains.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Structured data
helps companies manage customer information, track interactions, and segment
their customer base for marketing efforts.
E-commerce: Structured data is used for online sales, order
processing, and tracking customer purchases.
Healthcare Records: Electronic health records (EHRs) contain
structured patient information, making it easier for healthcare providers to
manage patient data.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment